Category: Tutorials

The best Angular alternatives in 2026 are React, Vue.js, Svelte, SolidJS, Vaadin, Next.js, Qwik, Astro, Ember.js, and Blazor. Each offers distinct advantages over Angular — from React's flexible component model and Svelte's compile-time performance to Vaadin's full-stack Java platform that eliminates the need for JavaScript entirely. Below, we compare all 10 Angular alternatives across performance, learning curve, enterprise readiness, and full-stack capabilities to help you choose the right Angular replacement for your project.

The Most Popular Java Frameworks in 2026: A Complete Guide
The Java frameworks your team picks determine how fast you ship, how well your systems scale, and how productive your developers are day to day. Here's a comprehensive look at the Java framework landscape in 2026 — and where Vaadin fits in. The Short Answer: Spring Boot Leads, but That's Not the ...

Extending Vaadin’s pure Java experience to the browser
A lot of the productivity and performance of Vaadin originates from the ability to use pure Java, utilizing the full Java ecosystem and executing your app with the JVM. When one needs to break the abstraction provided by Vaadin Flow, built-in components, and widely available add-ons, one enters the ...

Deploying a Java App for €3/Month: The Full JVM Hosting Guide
This post will detail a low-level, hands-on approach to deploying a full-featured Java application. There are several methods for deploying Java applications, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. These can be broadly categorized into the following three approaches: JVM hosting on a ...

3 Ways to Remove Browser Chrome and Go Fullscreen in Java Web Apps
Imagine your Java web application running without browser toolbars or navigation bars—just pure, focused content filling the entire screen. This guide reveals three proven methods to eliminate browser chrome in Vaadin applications, from zero-code solutions to Progressive Web Apps and the Fullscreen ...
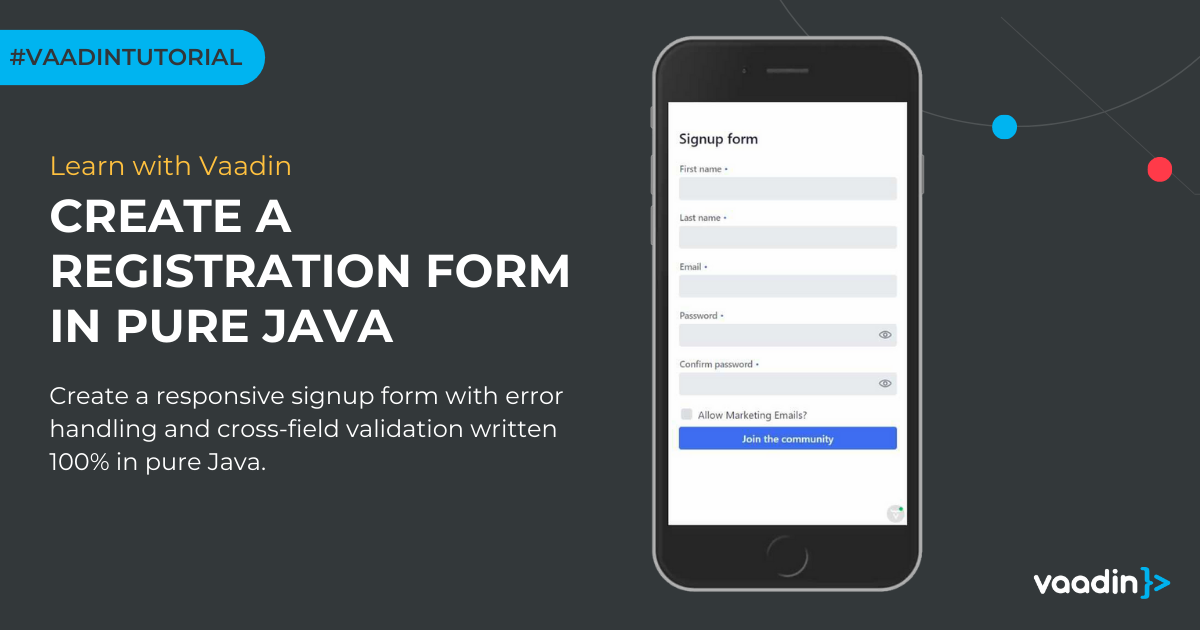
How to create a user registration form in pure Java
Learn how to create a responsive signup form with error handling and cross-field validation written in pure Java. Last updated September 2024. In this guide, we create a standard registration form with error handling and cross-field validation. This signup form is developed entirely in pure Java ...

How to use Visual Studio Code with Java and Maven projects
Last updated September 2024. Java is one of many languages supported by Visual Studio Code (VS Code). Like most things in VS Code, Java support is extension-based. You may need several extensions, depending on the project type and stack you are working with. You can find more detail in Java in ...

Consuming GraphQL APIs from Java applications
Updated for 2024. GraphQL has become a common alternative to REST as a way to provide data to modern web applications. They both solve the same problem, but GraphQL comes with a different set of trade-offs. It is designed to answer challenges pertinent to larger organizations, such as inter-team ...
.png)
Building an OpenAI-powered chatbot in Java
Updated in August 2024. Want to build a better version of ChatGPT? Learn how to integrate OpenAI's Chat Completions API to add an intelligent chatbot to your Vaadin Flow chat application. Create a new chat app with OpenAI chatbot integration Using the service at start.vaadin.com, create a new ...

Consuming REST services from Java Spring Boot applications
Using REST services is still the de facto way of providing data to traditional front-end applications. They often act as a "public API" for third-party solutions like mobile apps or as a "persistence layer" for client-side web apps (React, Vue, etc.). Java is probably the most common platform for ...





